Introduction
Regardless of size or industry, every organization relies heavily on data to drive decisions, serve customers, and maintain a competitive advantage. As the volume and value of data grow, so does the need to protect it from evolving threats. Businesses must recognize that data protection is not merely an IT responsibility but a core component of operational strategy. In the era of rapid digital transformation, safeguarding organizational data is an imperative, not an option. Data loss due to hardware failure, cyberattacks, or human error can cripple operations, disrupt service continuity, and damage business reputation. Deploying robust backup strategies, empowered by modern technologies and best practices, is essential for building resiliency and ensuring continual data availability. Solutions such as Cohesity enable organizations to streamline data backup, recovery, and management, helping them strengthen defenses against emerging data threats while simplifying operations.
The backup landscape constantly evolves with the advent of AI-based management, immutable storage, and sophisticated cloud integrations. Companies leveraging these tools with proven approaches can outpace risks and set the foundation for business continuity. A future-ready strategy isn’t defined solely by infrastructure choice, but by how businesses plan, test, and secure their data, end-to-end, with innovative backup and recovery solutions at its core.
Understanding the 3-2-1 Backup Rule
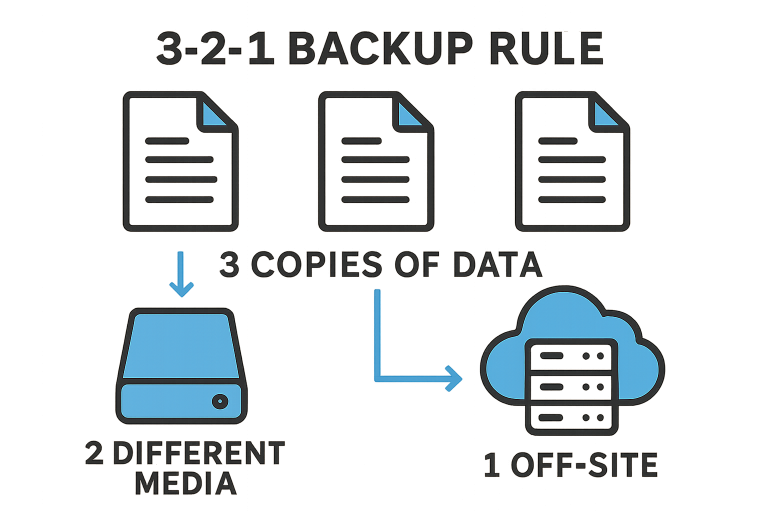
The 3-2-1 backup rule is widely regarded as a gold standard in data protection. The strategy prescribes maintaining at least three total copies of your data, stored on at least two different types of media, with one copy kept off-site. This approach drastically reduces the risk of catastrophic loss and ensures that data can be retrieved even if the primary infrastructure fails.
- Three copies ensure redundancy. If one is compromised, two additional copies remain.
- Two media types (such as disk and tape, or a combination of local storage and the cloud) guard against media-specific failure.
- One off-site copy protects against physical disasters at the primary location.
This principle underpins modern backup frameworks and helps businesses guard against everything from everyday mishaps to major disasters. Industry leaders like Zmanda provide excellent, in-depth guidance on the practical implementation of this strategy and its importance in fortifying data resiliency.
Embracing Immutable Backups
As ransomware and targeted cyberattacks become more sophisticated, immutable backups have become a cornerstone of modern data protection. Once created, these backups cannot be altered or deleted for a predetermined period. Immutability ensures backup data remains untainted and recoverable even if production systems or credentials are compromised.
By integrating immutable storage into backup routines, businesses gain an impenetrable line of defense. It is a critical safeguard for industries subject to strict compliance and regulatory requirements. It offers assurance that mission-critical data can be restored after an attack, without risk of malicious tampering or deletion.
Leveraging AI for Predictive Maintenance
Machine learning and AI technologies are reshaping backup architectures through predictive analytics, anomaly detection, and intelligent automation. These systems analyze historical data and real-time operations, flagging unusual patterns or performance indicators that may precede hardware failures or data inconsistencies.
By leveraging AI-driven tools, IT teams can anticipate and address potential issues before they disrupt operations. Predictive maintenance minimizes unplanned downtime, reduces reactive troubleshooting, and keeps the backup environment reliably available for swift recovery when needed—a clear step forward in operational maturity.
Implementing Hybrid Cloud Backup Solutions
Hybrid cloud backup strategies blend the strengths of on-premises and cloud-based storage. This dual approach equips businesses with the rapid restore capability of local backups and the redundancy and scalability that cloud repositories offer. When local interruptions or disasters strike, cloud backups act as a reliable off-site safety net.
Enterprises benefit from the agility to scale storage without physical infrastructure expansion and from the assurance that critical data is sheltered from site-specific risks. For an in-depth look at the advantages and implementation considerations of this approach, consult Gridheart’s article on hybrid cloud backup.
Regular Testing and Validation
A backup is only as dependable as its restore process. Consistent, realistic testing and validation are critical to ensuring that both the backup data and the restore procedures function seamlessly when an actual disaster emerges. Testing should simulate various failure scenarios, from accidental deletions and software errors to widespread outages or cyber incidents.
Routine validation builds organizational confidence in the backup environment, identifies process gaps, and ensures compliance with data retention and recovery mandates. A rigorous test schedule turns theoretical backup plans into actionable, effective disaster recovery playbooks.
Adopting Zero-Trust Security Measures
Zero-trust security combines strict identity verification, least-privilege access, and continuous monitoring to ensure only authorized personnel can interact with sensitive backup data. In this model, no device or user—internal or external—is automatically trusted. Every access request is scrutinized, authenticated, and logged.
Incorporating zero-trust principles into the backup ecosystem thwarts insider threats, credential misuse, and adversaries’ lateral movement. It complements technical security controls like encryption and immutability, creating a comprehensive defense-in-depth posture for data resilience.
Staying Informed on Emerging Technologies
The backup and disaster recovery field is rapidly evolving. Companies driven to resilience should keep abreast of advancements in areas like AI-enabled data management, next-gen encryption, distributed ledger solutions, and automated compliance reporting. Regular engagement with industry forums, technology publications, and thought leaders helps businesses anticipate changes and capitalize on innovation before threats surface.
Continuous improvement, professional development, and knowledge sharing are essential practices that empower teams to recognize risk, respond decisively in crises, and ensure recovery readiness as technology and threat landscapes change.
By adopting layered, forward-looking data backup strategies rooted in industry best practices and enhanced by modern technologies, organizations can protect their critical digital assets and ensure operational continuity, even in the face of unpredictable challenges.







