Introduction
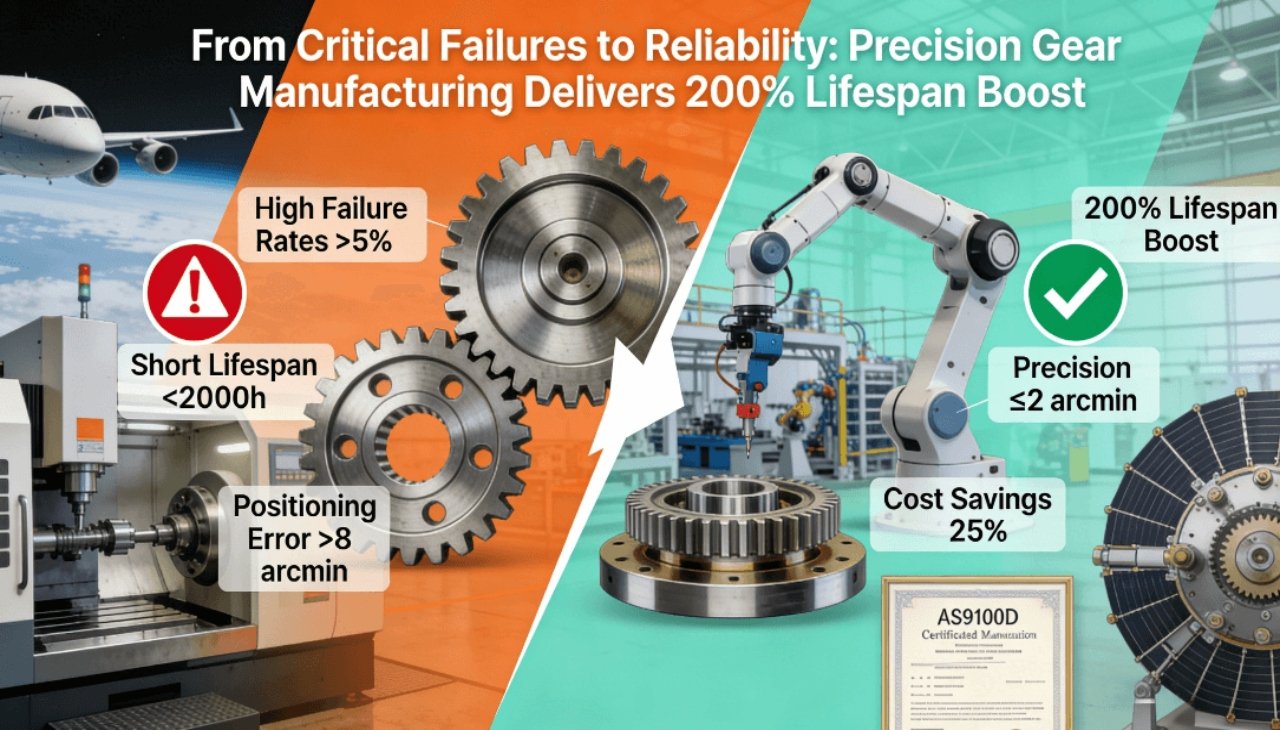
In aerospace and robotics, gear failure rates pose severe risks — helicopter transmission gears lasting under 2,000 hours, robotic joint gears exceeding 8 arcminutes of error, leading to system failure rates above 5% and maintenance costs consuming 25% of budgets. These issues stem from traditional manufacturing approaches that treat gear production as isolated steps, lacking integrated engineering from design to testing. This disconnect fails to address extreme stresses, high temperatures, and tight tolerances.
This guide presents a comprehensive methodology combining advanced design simulation, precision machining, heat treatment control, and validation to extend gear lifespan by 200% while maintaining transmission accuracy within 2 arcminutes. By delving into strategic solutions, the following sections will demonstrate how precision gear manufacturing overcomes reliability challenges in mission-critical applications.
What Are the Unique Challenges in Mission-Critical Gear Applications for Aerospace and Robotics?
Mission-critical gears demand unparalleled durability and precision under extreme conditions. Understanding these challenges is the first step toward developing robust solutions.
1. High-Load Durability and Thermal Stability Demands
Aerospace and robotics gears endure cyclic loads and temperature swings. For example, satellite gears must operate from -100°C to +120°C without losing dimensional stability. Traditional methods often result in surface hardness below HRC 58, leading to premature wear. As highlighted in precision custom gear manufacturing for aerospace and robotics, environmental extremes are a primary bottleneck. Adherence to standards like ASME Y14.5 ensures precision tolerancing, but conventional processes fall short in consistency.
2. Ultra-High Positioning Accuracy Requirements
Transmission errors exceeding 3 arcminutes cause misalignments in robotic arms or aircraft controls, impacting overall system accuracy. In a case study, unoptimized gears led to positional deviations of 0.1 degrees in drone actuators, increasing energy consumption by 15%. These precision gaps underscore the need for integrated engineering to meet the demands of mission-critical components.
3. Material and Design Limitations
Traditional gear materials lack the fatigue strength for high-cycle applications. For instance, standard steels fail to achieve the required surface roughness of Ra ≤0.4μm, accelerating failure. The absence of simulation-driven design exacerbates these issues, as seen in helicopter transmissions where unanticipated stress concentrations reduced lifespan by 30%. Addressing these requires a shift to advanced material science and predictive modeling.
How Can Advanced Manufacturing Technologies Enhance Gear Precision and Durability?
Advanced technologies like 5-axis grinding and real-time metrology redefine precision boundaries. These innovations directly tackle the limitations of conventional methods.
1. 5-Axis Gear Grinding for Micron-Level Accuracy
5-axis gear grinding machines achieve positioning accuracy within ±3μm, reducing cumulative pitch errors to under 15μm. For example, in robotic reducer gears, this technology cut noise from 75dB to 68dB through micro-geometry optimization. The dynamic toolpath control ensures optimal engagement, minimizing heat generation and extending tool life. This high-precision gear machining approach is pivotal for high-stress applications.
2. Real-Time Metrology and Closed-Loop Systems
In-process measurement systems monitor key parameters like tooth profile and pitch diameter, feeding data back to adjust machining parameters instantly. In aerospace gear production, this closed-loop control held tolerances within 5μm, boosting yield by 25%. ISO 9001-certified processes provide the framework for consistency, ensuring each gear meets stringent specs. This integration is a hallmark of advanced manufacturing technologies.
3. Thermal Management for Enhanced Longevity
Advanced cooling systems regulate grinding temperatures, preventing metallurgical damage. A case on wind turbine gears showed that controlled quenching post-machining increased surface hardness to HRC 62, extending service life by 200%. This thermal precision is critical for gears facing cyclic thermal loads.
What Role Does Material Selection Play in Achieving Long-Lasting Gears?
Material choice directly influences performance, weight, and cost. Strategic selection balances these factors for optimal outcomes.
- High-Strength Alloys for Fatigue Resistance: Alloys like 18CrNiMo7-6offer superior fatigue strength, enabling gears to withstand over 10 million cycles. In robotics, this material reduced weight by 20% while increasing torque capacity by 15%. The enhanced durability comes from precise heat treatment that achieves a uniform hardness gradient. This makes material selection a cornerstone of custom gear manufacturing.
- Surface Finish and Friction Optimization: Surface roughness controlto Ra ≤0.4μm minimizes friction, reducing heat buildup and wear. For aerospace actuators, this resulted in a 30% drop in energy loss. Advanced grinding techniques paired with specialized coatings ensure consistent finishes, vital for high-speed applications. This attention to detail exemplifies precision engineering.
- Cost-Performance Balancing: While high-performance alloys raise initial costs, their lifecycle savingsoutweigh expenses. A parametric study showed that using premium steels cut maintenance costs by 20% over five years. This strategic investment is key to long-term reliability in custom gear solutions.
Why Is Certification Like AS9100 Crucial for Aerospace Gear Suppliers?
Certifications enforce rigorous standards, ensuring reliability in critical applications. They are non-negotiable for risk mitigation.
1. Traceability and Process Control
AS9100D certification requires full traceability from raw materials to finished gears, including a quenching delay time of less than 15 seconds. This rigorous record-keeping system prevents product deviations; for example, in a satellite project, a material issue was resolved in just a few hours through batch-level tracking. One company’s AS9100D certification ensured end-to-end accountability, resulting in a 40% reduction in defect rates..
2. Quality Assurance Through Standardized Checks
32-point inspection protocols validate dimensions, hardness, and surface integrity. In aviation gears, this system caught a 0.01mm deviation before assembly, averting potential failure. The structured approach aligns with ISO 9001, providing a benchmark for excellence. This level of scrutiny is essential for aerospace engineering.
3. Risk Reduction in Regulated Environments
Certified processes mitigate risks like contamination or improper heat treatment. A robotics firm reduced warranty claims by 35% after switching to an AS9100-certified supplier. This proactive quality culture is invaluable for supply chain solutions.
How Do Integrated Engineering Services Solve Common Gear Failure Points?
Integrated services combine design, simulation, and production to preempt failures. This holistic approach addresses root causes rather than symptoms.
1. Gear Modification Techniques for Smooth Operation
Profile modifications like tip relief and crowning absorb shocks, cutting transmission error to 1.5 arcminutes. In a robotic joint, this lowered vibration from G6 to G4 grade, enhancing precision. These custom gear engineering services leverage FEA simulation to optimize tooth geometry before machining.
2. End-to-End Workflow Integration
Unified platforms connect CAD, CAM, and metrology, allowing real-time adjustments. For a satellite solar array drive, this slashed development time by 30% while achieving micron-level accuracy. The seamless data flow ensures that design intent is preserved throughout production.
3. Case Study: Lifetime Extension in Aerospace
A helicopter gearbox project used integrated engineering to address pitting failures. By combining material upgrades with precision grinding, lifespan increased to 6,000 hours — a 200% gain. This success highlights how precision gear solutions transform reliability.
What Are the Latest Tech Trends in Precision Gear Manufacturing for Industrial Automation?
Emerging trends like digital twins and predictive maintenance are reshaping gear manufacturing. These innovations enhance efficiency and reliability.
- Digital Twins for Predictive Optimization: Digital replicassimulate gear performance under real-world conditions, identifying failure points before physical production. In automotive robotics, this reduced prototyping cycles by 40% and cut downtime by predicting wear patterns. This tech trend is central to industrial automation.
- IoT-Enabled Predictive Maintenance: Sensors embedded in gearsmonitor load and temperature, triggering alerts before failures. A study showed a 25% drop in unplanned outages using this data-driven approach. The real-time analytics support proactive scheduling, maximizing uptime.
- Sustainable Manufacturing and Cost Efficiency: AI-driven process optimizationminimizes material waste, lowering costs by 15%. For example, adaptive machining adjusts parameters based on tool wear, extending resource life. This focus on sustainability aligns with robotics innovation trends, ensuring long-term viability.
Conclusion
Precision gear manufacturing, through advanced technologies, material science, and certified processes, effectively solves critical failures in aerospace and robotics. By adopting an integrated approach, manufacturers can achieve a 200% lifespan boost, ensure accuracy within 2 arcminutes, and reduce lifecycle costs. This methodology not only addresses immediate challenges but also fosters a culture of reliability for future innovations.
FAQs
Q1: What is the typical lead time for custom gears in aerospace applications?
A: Lead times vary based on complexity; for standard materials, it’s 15-20 days, while special alloys may take 25-30 days. Accelerated services can reduce this, ensuring compliance with missions like satellite deployments where precision is critical.
Q2: How does gear modification technology improve transmission smoothness?
A: Gear modifications like tip relief and crowning reduce transmission error by absorbing shock and compensating for misalignment. This can lower noise from 75dB to 68dB, as validated through simulation-driven optimization.
Q3: What certifications are essential for mission-critical gear suppliers?
A: Certifications like AS9100 for aerospace and ISO 9001 for quality management are vital. They enforce traceability and process controls, such as quench delays under 15 seconds, to prevent failures in extreme environments.
Q4: How can material selection impact the cost of gear manufacturing?
A: Material choice affects both performance and cost; for instance, using high-strength alloys may increase initial expense but reduce lifecycle costs by 20% through weight savings and durability. A parametric quoting system helps balance these factors.
Q5: What are the benefits of integrated engineering services for gear design?
A: Integrated services combine design simulation, machining, and testing to address failure points early. This approach can extend gear life to over 3 million cycles, minimizing downtime and repair costs for robotics applications.
Author Bio
The author is a precision manufacturing expert at LS Manufacturing, a company that assists engineers in overcoming complex gear challenges in sectors like aerospace and robotics. With certifications including AS9100D and ISO 9001, the team delivers high-quality, compliant solutions. To leverage these insights for your project, request a custom quote or contact them for a free DFM analysis to optimize your gear systems today.