Introduction
Software testing is a crucial process in the development of software applications and its main goal is to identify defects, errors, or bugs within the software. It involves executing the software under controlled conditions and analyzing its behavior to determine if it meets the specific requirements and produces the expected results.
The primary objective of software testing is to ensure the quality and reliability of the software by identifying any issues that may affect its performance, functionality, security, or usability. By detecting and fixing these issues early in the development cycle, software testing helps in enhancing the overall quality of the software and reduces the risk of failures or malfunctions when it is deployed to users.
Types of software testing
Manual Testing
Manual testing is a software testing approach in which testers execute test cases and procedures manually, without the aid of automation tools or scripts. To replicate user actions, explore different scenarios, and verify the expected behavior of the software or system being tested, human intervention is required.
To validate various parts of the product during manual testing, testers adhere to a predefined set of test cases, test scripts, or test scenarios. They interact with the system, entering various pieces of data, and comparing the outcomes to what was anticipated. Manual testing can involve functional testing, usability testing, regression testing, system integration testing, and various other types of testing.
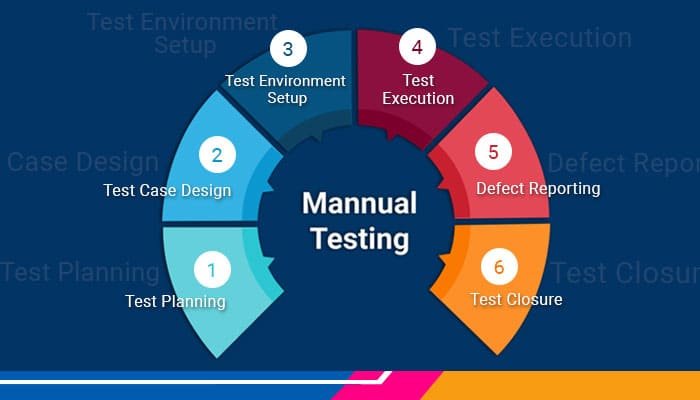
The process of manual testing typically involves the following steps
Test planning
Testers analyze the software requirements and specifications, to identify the scope of testing, create test cases, and define test objectives.
Test case design
Testers create thorough test cases that specify the actions to be taken and the anticipated results.
Test environment setup
Setting up the necessary test environment including installing the software, configuring the hardware and network settings, and ensuring all essential resources are available.
Test execution
Testers execute the test cases manually, following the specified steps and documenting any deviations or issues encountered.
Defect reporting
If any defects or discrepancies are identified during testing, testers report them to the development team using a bug-tracking system. They provide detailed information about the issue, including steps to reproduce it.
Test closure
Once the testing is complete, testers analyze the test results, prepare test closure reports, and provide feedback on the quality of the software.
Manual testing offers several advantages, such as
Exploratory testing
Testers can use their experience, intuition, and creativity to explore the software and uncover unexpected defects or usability issues.
Adapting to changes
Manual testing allows flexibility in adapting to changing requirements and making on-the-fly decisions during the testing process.
User perspective
Testers can assess the software’s usability, user interface, and overall user experience from a human perspective.
However, manual testing also has some limitations, including
Time-consuming
Manual testing can be time-consuming, especially for large and complex software systems.
Human error
Manual testing relies on human skills and judgment, making it prone to errors and inconsistencies.
Costly
As manual testing requires human resources, it can be more expensive compared to automated testing in the long run. Despite these limitations, manual testing remains an essential part of the software testing lifecycle, often used in combination with automated testing techniques to ensure comprehensive test coverage and deliver high-quality software products.
Automation Testing
Automation testing refers to the process of using software tools and scripts to execute test cases automatically, without the need for manual intervention. It is a technique employed in software development and quality assurance to verify the functionality, reliability, and performance of a software application.
In automation testing, test scripts are created to simulate user interactions with the application under test. These scripts can be written in various programming languages or by using specialized testing frameworks. The purpose of automation testing is to streamline the testing process, increase efficiency, and reduce the time and effort required for repetitive and tedious manual testing.
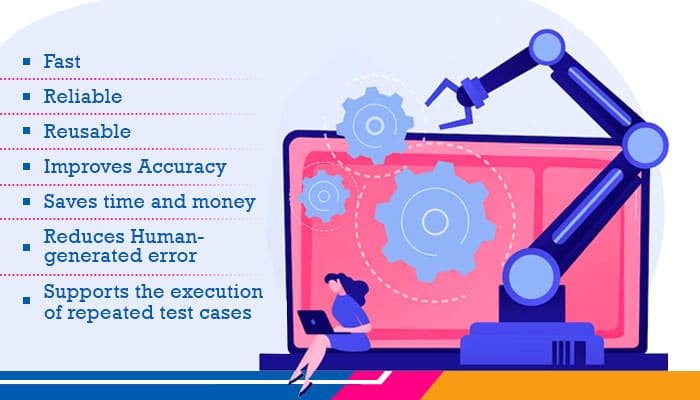
Automation testing offers several benefits
Faster and efficient testing
Automated tests can execute repetitive tasks much faster than manual testers, allowing for more thorough testing within a shorter time frame. This efficiency is especially useful for large-scale or complex applications.
Improved test coverage
Automation enables the execution of a large number of test cases and scenarios that may be impractical or time-consuming to test manually. It helps achieve better test coverage and reduces the chances of missing critical defects.
Regression testing
Automated tests are particularly valuable for performing regression testing, where previously tested functionality is retested to ensure that recent changes or updates have not introduced new issues. Automation can quickly rerun regression test suites, ensuring that existing functionality remains intact.
Reusability
Automation scripts can be reusable, allowing test cases to be easily executed on different versions or builds of the software. This reusability saves time and effort in maintaining and updating test suites as the application evolves.
Accuracy and consistency
Automation cuts out the possibility of human error that can occur during manual testing, ensuring consistent and accurate test execution. It helps in reducing subjective judgment and producing reliable test results.
However, it’s important to note that automation testing is not a substitute for manual testing entirely. Manual testing is still necessary for exploratory testing, usability testing, and certain scenarios that require human judgment and intuition. Automation testing is most effective when used in conjunction with manual testing to achieve comprehensive test coverage and ensure high-quality software products.
Conclusion
Software testing can be performed manually or using automated testing tools, depending on the complexity of the software and the available resources. Both approaches have their advantages and are often used in combination to achieve thorough testing coverage.
Overall, software testing plays a vital role in ensuring that software applications are reliable, functional, and meet the intended requirements, thereby enhancing user satisfaction and minimizing the risks associated with software defects.